Northwest well with downhole pump production monitoring and interpretation with distributed fiber optic system
Pump the photoelectric composite cable into the well
Two production wells in Southwest China of PetroChina adopt segmented hydraulic fracturing technology, the operator have a strong demand for understanding the indicators of underground fracturing fractures. The tool string consisting of fiber optic cables, torpedo type optoelectronic cablehead, CCLs, and other downhole tools to pump into two adjacent wells. DTS and DAS data were acquired to monitor hydraulic fracture signals. By correcting and interpreting fracturing data, we provide customers with information on the changes in hydraulic and natural fractures during the fracturing process.

On site construction situation(L)Insert torpedo head protection at the end of the optical cable(R)
Continuous health check of the in-well optical fibers
Due to the high underground temperature of 140 ℃ and the fiber optic monitoring time of up to 60 days, the quality of the fiber optic cable is put to test. Feibo Optoelectronics used the OTDR measurement for the two optical composite cables entering the well at regular intervals and saves the data for comparison to ensure the quality of fiber optic data acquisition.
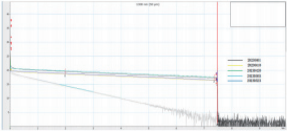
Fiber OTDR curve
Monitoring of neighboring well strain signals
During hydraulic fracturing, optical fibers are pumped and pre-set in adjacent wells of the fracturing well. With the injection of fracturing fluid and the formation of cracks, when the cracks reach the adjacent well, the rocks around the wellbore will be subjected to compression and tension, causing the optical fiber to be subjected to stress changes in the casing. By monitoring these strain changes, real-time information such as fracture propagation, stimulation effect, and wellbore integrity can be obtained. DAS interprets the morphology of fracture development and evaluates the effectiveness of downhole fracturing by monitoring the ultra low-frequency vibrations generated by these stresses.
As the amount of injection fluid gradually increases during fracturing, the fractures continue to change and extend. The strain signal reached by the fractures can be observed in the monitoring well (adjacent well). The following figure shows the relationship between the total pumping amount of each fracturing section and the arrival of the crack strain signal (the red font indicates the fracturing sections with weak or unobserved strain signals)
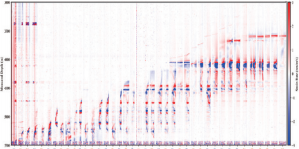
Overview of Strain Rate Signal Diagram
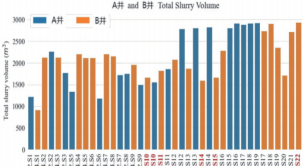
Total injection amount for each fracturing section

 Prev
Prev
 Next
Next
 To list
To list